Conditions Basics
What is cholecystitis?
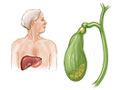
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, a small organ near the liver that plays a part in digesting food. Normally, fluid called bile passes out of the gallbladder on its way to the small intestine. If the flow of bile is blocked, it builds up inside the gallbladder, causing swelling, pain, and possible infection.
What causes it?
A gallstone stuck in the cystic duct, a tube that carries bile from the gallbladder, is most often the cause of sudden (acute) cholecystitis. The gallstone blocks fluid from passing out of the gallbladder. This results in an irritated and swollen gallbladder. Infection or trauma, such as an injury from a car accident, can also cause cholecystitis.
Acute acalculous cholecystitis, though rare, is most often seen in critically ill people in hospital intensive care units. In these cases, there are no gallstones. Problems from another severe illness, such as heart disease, diabetes, or an impaired immune system, cause the swelling.
Long-term (chronic) cholecystitis is another form of cholecystitis. It occurs when the gallbladder remains swollen over time, causing the walls of the gallbladder to become thick and hard.
What are the symptoms?
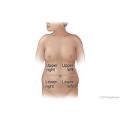
The most common symptom of cholecystitis is pain in your upper right abdomen that can sometimes move around to your back or right shoulder blade. Other symptoms include:
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Tenderness in the right abdomen.
- Fever.
- Pain that gets worse during a deep breath.
- Pain for more than 6 hours, particularly after meals.
Older people may not have fever or pain. Their only symptom may be a tender area in the abdomen.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam. Your doctor will carefully feel your right upper abdomen to look for tenderness. You may have blood drawn and an ultrasound, a test that uses sound waves to create a picture of your gallbladder. Ultrasound may show gallstones, thickening of the gallbladder wall, extra fluid, and other signs of cholecystitis. This test also allows doctors to check the size and shape of your gallbladder.
You may also have other tests, such as a gallbladder scan. This is a nuclear scanning test that checks how well your gallbladder is working. It can also help find blockage in the tubes (bile ducts) that lead from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine (duodenum).
How is cholecystitis treated?
Treatment for cholecystitis will depend on your symptoms and your general health.
The main way to treat this disease is surgery to remove the gallbladder. This surgery can often be done through small cuts (incisions) in the belly. This is called a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In some cases, you may need a more extensive surgery.
You may need surgery as soon as possible. The doctor may try to reduce swelling and irritation in the gallbladder before removing it. You may be given fluids and antibiotics through an I.V. You may also be given pain medicine.
If you are not able to have surgery or cannot have it right away, the doctor may put a tube in the gallbladder to drain the bile.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: October 6, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 6, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.