What is deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
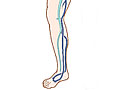
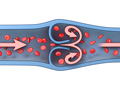
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot (thrombus) in a deep vein, usually in the legs. These clots require medical care right away.
These clots are dangerous because they can break loose, travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, and block blood flow in the lungs (pulmonary embolism). Pulmonary embolism is often life-threatening. DVT can also lead to long-lasting problems. It may damage the vein and cause the area near the clot to ache, swell, and change color.
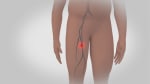
Blood clots most often form in the calf and thigh veins, and less often in the arm veins or pelvic veins. Diagnosis and treatment of DVT in other parts of the body are similar.
What causes it?
Causes of a blood clot in a deep vein (DVT) include slowed blood flow, which can happen when you're not active for long periods of time, and abnormal clotting problems, which make the blood clot too easily or too quickly. Surgery or an injury to the blood vessels can also cause a blood clot.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of DVT include swelling of the affected leg or arm. The leg or arm may swell, feel warm, or look red. The calf or thigh may ache or feel tender. Pain may get worse and last longer or become constant. If a blood clot is small, it may not cause symptoms.
How is it diagnosed?
If your doctor thinks that you have DVT, you probably will have an ultrasound test to help find any clots that might be blocking your blood flow. More tests may be used when ultrasound results are unclear. You'll also have a physical exam, and the doctor will ask you questions about your past health.
How is DVT treated?
Treatment for DVT usually involves taking blood thinners (anticoagulants) for at least 3 months. How long you take them depends on your health, where the blood clot is, and your risk for a pulmonary embolism. At home, you can take walks and you can prop up or elevate your leg or arm.
How can you prevent DVT?
To help prevent DVT, you might take an anticoagulant medicine. After an illness or surgery, you can try to get up and out of bed often. You might wear compression stockings. You may try leg exercises that can help blood flow.
Cause
Causes of a blood clot in a deep vein (DVT) include:
- Slowed blood flow. This can happen when you're not active for long periods of time. For example, clots can form if you are paralyzed, are confined to bed, or must sit while on a long flight or car trip.
- Abnormal clotting problems that make the blood clot too easily or too quickly. This may be caused by certain health problems, such as cancer or a genetic clotting disorder. Pregnancy, hormonal birth control, and hormone therapy can also make blood more likely to clot.
- Surgery or an injury to the blood vessels. Blood is more likely to clot in veins shortly after they are injured.
What Increases Your Risk
Many things increase your risk for DVT. These include:
- Being older than 40.
- Being overweight.
- Not taking anticoagulant medicine as prescribed.
- Having to stay in bed for more than 3 days (such as in a hospital).
- Sitting for a long time, especially when traveling long distances.
- Being pregnant, using hormonal birth control, or using hormone therapy.
- Having a recent surgery or injury that involved the legs, hips, belly, or brain.
- Having certain health problems, such as cancer, blood vessel disease, or an inherited clotting disorder.
- Smoking.
Prevention
- Exercise your lower leg muscles to help blood flow in your legs. Point your toes up toward your head so the calves of your legs are stretched, then relax and repeat. This is a good exercise to do when you are sitting for long periods of time.
- Get out of bed as soon as you can after an illness or surgery. If you need to stay in bed, do the leg exercise noted above every hour when you are awake.
- Use special stockings called compression stockings. These stockings are tight at the feet with a gradually looser fit on the leg. Many doctors recommend that you wear compression stockings during a journey longer than 8 hours.
- Take breaks when you are on long trips. Stop the car and walk around. On long airplane flights, walk up and down the aisle hourly, and flex and point your feet every 20 minutes while sitting.
- Take blood-thinning medicines after some types of surgery if your doctor recommends it. Blood thinners also may be used if you are likely to develop clots.
Learn more
Watch
Symptoms
DVT often doesn't cause symptoms. Or it may cause only minor ones. When symptoms happen, they include:
- Swelling in the affected area of the leg or arm.
- Redness and warmth in the affected area.
- Pain or tenderness. You may have pain only when you touch the affected area or when you stand or walk.
Sometimes a pulmonary embolism is the first sign that you have DVT.
If your doctor thinks you may have DVT, you will probably have an ultrasound test. You may have other tests as well.
What Happens
A blood clot in a deep vein (DVT) may break loose. It if does, it can travel to the lungs and block blood flow (pulmonary embolism). This is an emergency.
The risk of a pulmonary embolism can depend on the location of the blood clot. A pulmonary embolism is more likely if a blood clot is at or above the knee than if it is in the calf. But a blood clot in a calf also has a chance of causing a pulmonary embolism.
After the first time you have DVT, there is a risk of having blood clots again. Your risk can depend on what caused the clot and how it was treated. Your doctor will treat you to try to prevent clots from happening again.
If you have had DVT, you have a risk of a painful complication called post-thrombotic syndrome. Anticoagulant medicine may help lower the risk of this complication.
Learn more
When to Call a Doctor
Call 911 or other emergency services if you have pulmonary embolism symptoms, including:
- Sudden shortness of breath.
- Sharp chest pain that sometimes gets worse with deep breathing or coughing.
- Coughing up blood.
- Fainting.
- Rapid pulse or irregular heartbeat.
- Anxiety or sweating.
Call your doctor now if you have DVT symptoms, including:
- Swelling, warmth, or tenderness in the soft tissues of your leg. Swelling may also appear as a swollen ridge along a blood vessel that you can feel.
- Pain in your leg that gets worse when you stand or walk. This is especially important if there is also swelling or redness in your leg.
Exams and Tests
If your doctor thinks that you have DVT, you probably will have an ultrasound test to measure the blood flow through your veins and help find any clots that might be blocking the flow.
To see if you need an ultrasound, the doctor will do a physical exam. This will include checking your heart and lungs and checking your legs for pain, tenderness, warmth, swelling, bulging veins, or changes in skin color.
More tests may be used when ultrasound results are unclear. These can include a D-dimer blood test, MRI, or CT scan. These tests may help diagnose or exclude a blood clot.
If your doctor thinks you might have a pulmonary embolism, the doctor may test your lungs.
Learn more
Watch
Treatment Overview
The main goals of treatment for DVT are:
- To prevent the blood clot from getting larger while the body reabsorbs it.
- To prevent the blood clot from traveling to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- To prevent post-thrombotic syndrome. This is a condition that can cause pain, sores, and swelling of the affected leg.
- To prevent blood clots from coming back.
Treatment includes medicine and self-care.
Blood thinners
DVT is usually treated with anticoagulant medicines. These medicines are often called blood thinners, but they don't actually thin the blood. They prevent blood clots by increasing the time it takes a blood clot to form. Blood thinners also help prevent existing blood clots from becoming larger while the body slowly reabsorbs them.
You might take anticoagulants for at least 3 months. The length of time will vary based on your own health and your risk for a pulmonary embolism.
Other treatments
Other treatments may be used in the hospital for some people. These treatments include thrombolytic medicine, a procedure to remove the blood clot (thrombectomy), and vena cava filters. But these treatments aren't common. They might be used for people who are at risk for serious problems from DVT.
Self-care
Your doctor may also recommend self-care to relieve symptoms. This care includes:
- Walking several times a day.
- Propping up (elevating) your leg or arm.
- Wearing compression stockings.
Learn more
Self-Care
Home treatment for DVT focuses on:
- Taking anticoagulants (blood thinners) safely.
- Relieving symptoms.
You can do a few things to treat your DVT at home.
- Take anticoagulants safely. If you take an anticoagulant medicine, also called a blood thinner, you need to take extra steps to avoid bleeding problems.
- Prevent falls and injuries.
- Tell your doctors about all other medicines, supplements, and vitamins that you take.
- Get regular blood tests, if your doctor tells you to.
- Keep your diet the same. What you eat can affect the way your blood thinner works. So eat a consistent diet. It's most important to eat the same amount of foods that are lower in vitamin K because it can affect the way the blood thinner works. Talk with your doctor before making any changes in your diet.
- Walk several times a day, if possible. Walking can help relieve symptoms like pain and swelling.
- Elevate your leg or arm. This also helps with pain and swelling.
- Wear compression stockings if your doctor recommends them. Compression stockings are specially fitted stockings. They are tightest at the foot. They get less and less tight farther up on your leg.
Your doctor might suggest that you take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as ibuprofen, to relieve pain. Do not take an NSAID unless your doctor tells you that it's safe for you because it may increase your risk for bleeding.
Learn more
Watch
Medicines
Anticoagulant medicines, also called blood thinners, are used to prevent and treat DVT.
These medicines prevent new clots from forming. They also prevent existing clots from getting larger. They don't get rid of existing clots.
Different types of anticoagulants are used. Talk with your doctor about which medicine is right for you.
If you are in the hospital, you might be given an anticoagulant as a pill, a shot, or in a vein through an I.V. After you go home, you might give yourself shots for a few days. For long-term treatment, you'll likely take a pill.
You might take anticoagulants for at least 3 months. You may take them for a much longer time, maybe even the rest of your life. The length of time will be based on your health and your risk for developing more blood clots or a pulmonary embolism.
Learn more
Watch
Credits
Current as of: October 2, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 2, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.