What is an ischemic stroke?
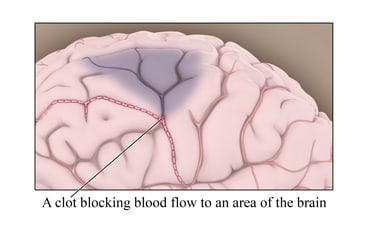
An ischemic (say "iss-KEE-mick") stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain. This means that blood cannot flow to some part of the brain. Without blood and the oxygen it carries, this part of the brain starts to die.
This is different from a hemorrhagic (say "heh-muh-RA-jick") stroke, which happens when a blood vessel in the brain has burst open or has started to leak.
The brain damage from a stroke starts within minutes. The part of the body controlled by the damaged area of the brain cannot work properly. Quick treatment can help limit damage to the brain and make recovery more likely.
The problems someone has after a stroke depend on what part of the brain was affected and how much damage the stroke caused. A stroke may affect movement and senses, speech, memory, thinking, or emotions. Stroke rehabilitation, which includes training and therapy, can help people recover.
What are the symptoms?
If you have any of these symptoms, call 911 or other emergency services right away:
- You have symptoms of a stroke. These may include:
- Sudden numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of movement in your face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of your body.
- Sudden vision changes.
- Sudden trouble speaking.
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding simple statements.
- Sudden problems with walking or balance.
- A sudden, severe headache that is different from past headaches.
- Fainting.
- A seizure.
Call 911 if you have symptoms that seem like a stroke, even if they go away quickly. You may have had a transient ischemic attack (TIA). A TIA is a warning that a stroke may happen soon. Getting early treatment for a TIA can help prevent a stroke.
What causes an ischemic stroke?
An ischemic stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks blood flow in the brain. Causes of blood clots include:
- Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis). This is caused by high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, or smoking.
- Atrial fibrillation.
How is ischemic stroke treated?
Emergency treatment may be done to restore blood flow to the brain using medicine or a procedure. Medicine and a heart-healthy lifestyle can help prevent another stroke. A stroke rehab program can help you recover and learn ways to adapt to changes caused by a stroke.
How can you help prevent another stroke?
- Work with your doctor to treat any health problems that raise your risk. These include atrial fibrillation, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
- Be safe with medicines. Take your medicine exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine.
- Have a heart-healthy lifestyle.
- Don't smoke, vape, or use other tobacco or nicotine products. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about quit programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good. Also avoid secondhand smoke and the aerosol mist from vaping.
- Limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day for men and 1 drink a day for women.
- Stay at a weight that's healthy for you. Talk to your doctor if you need help losing weight.
- Be active. Ask your doctor what type and level of activity is safe for you.
- Eat heart-healthy foods. These include vegetables, fruits, nuts, beans, lean meat, poultry, fish, and whole grains. Limit sodium and sugar.
- Get vaccinated against COVID-19, the flu, and pneumonia.
- If you think you may have a problem with alcohol or drug use, talk to your doctor.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter D161 in the search box to learn more about "Learning About an Ischemic Stroke".
Current as of: October 2, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

