What is it?
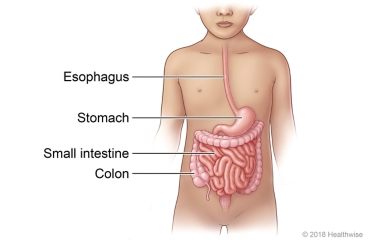
An upper gastrointestinal (GI) series looks at the upper and middle sections of the gastrointestinal tract. The test uses barium contrast material, fluoroscopy, and X-ray. Fluoroscopy is a kind of X-ray.
Why is this test done?
An upper GI series is done to find the cause of symptoms such as vomiting, burping up food, trouble swallowing, poor weight gain, bleeding, or belly pain. It's used to find narrow spots or blockages in the upper intestinal tract. The test can also find ulcers, polyps, and pyloric stenosis.
How do you prepare for the test?
The doctor may ask you to have your child do one or all of the following:
- Stop eating before the test. The doctor will tell you when your child should stop eating so that your child's stomach is empty for the test.
- Stop taking certain medicines.
You may want to bring a toy or favorite blanket for your child. You may also want to bring a snack or drink for after the test.
How is the test done?
- Your child will need to wear a hospital gown and take off any jewelry.
- Your child will lie on their back on an X-ray table.
- You will be able to stay with your child during the test (unless you are pregnant). You will need to wear a lead vest to protect from the X-rays.
- Your child will have an X-ray taken before drinking the barium mix. Then your child will take small swallows repeatedly during the series of X-rays that follow. (If your child can't drink the mix, the doctor may use a small, flexible tube to help get it down.)
- The doctor uses fluoroscopy and X-ray pictures to watch the barium pass through your child's GI tract. The table is tilted at different positions. Your child may change positions to help spread the barium.
- The test is over when the doctor has seen enough of the barium pass through your child's GI tract.
How long does the test take?
The test will take less than an hour. If your child is also having a small bowel study, the test may take 2 to 3 hours.
What happens after the test?
- Your child will probably be able to go home right away. Results of the test are usually ready in 1 to 3 days.
- Your child can go back to their usual activities right away. Your child may eat and drink whatever they like, unless the doctor says not to.
- It's a good idea for your child to drink a lot of fluids for a few days. This will flush out the barium.
- If your child is constipated after the test, they may be given a mild laxative to flush the barium out of the intestines. Be sure to talk to your doctor if your child isn't able to have a bowel movement within 2 to 3 days after the test.
- For 1 to 3 days after the test, your child's stool will look white from the barium.
Follow-up care is a key part of your child's treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if your child is having problems. It's also a good idea to keep a list of the medicines your child takes. Ask your doctor when you can expect to have your child's test results.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter U250 in the search box to learn more about "Upper GI Series: About Your Child's Test".
Current as of: March 26, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

