What is it?
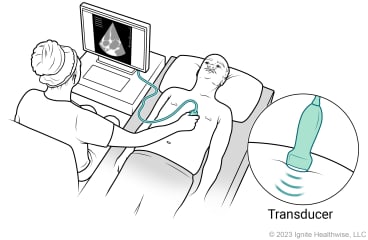
An echocardiogram (also called an echo) uses sound waves to make an image of your heart. A device called a transducer sends sound waves that echo off your heart and back to the transducer. These echoes are turned into moving pictures of your heart that can be seen on a video screen.
In a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), the transducer is moved across your chest or belly. A TTE is the most common type of echocardiogram.
Why is this test done?
This test is done to check your heart health. It's used for many reasons. For example, it may be done to:
- Check a heart murmur.
- Look for the cause of shortness of breath or unexplained chest pain or pressure.
- Check how well your heart is pumping blood.
- Check to see how well your heart valves are working.
- Look for blood clots inside your heart.
- Measure the size and shape of the heart's chambers.
- Measure the blood pressure and speed of blood flow through the heart.
How is the test done?
- You may be asked to remove your clothes above your waist. You may be given a cloth or paper covering to use during the test.
- You will lie on your back or on your left side on a bed or table.
- You may receive medicine through a vein (intravenously, or I.V.). The I.V. can be used to give you a contrast material. This helps your doctor get good views of your heart.
- Small pads or patches (electrodes) will be placed on the skin of your chest to record your heart rate during the test.
- A small amount of gel will be rubbed on the side of your chest to help pick up the sound waves.
- The transducer will be pressed firmly against your chest and moved slowly back and forth. It is usually moved to different areas on your chest or belly to get specific views of your heart.
- You will be asked to do several things, such as hold very still, breathe in and out very slowly, hold your breath, or lie on your left side.
- When the test is over, the gel is wiped off and the electrodes are removed.
What are the risks of the test?
There are no known risks from having this test.
- No electricity passes through your body during the test. There is no danger of getting an electrical shock.
- You do not receive any radiation.
What happens after the test?
- You will probably be able to go home right away. It depends on the reason for the test.
- You can go back to your usual activities right away.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to keep a list of the medicines you take. Ask your doctor when you can expect to have your test results.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter T235 in the search box to learn more about "Transthoracic Echocardiogram: About This Test".
Current as of: October 2, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

