Overview
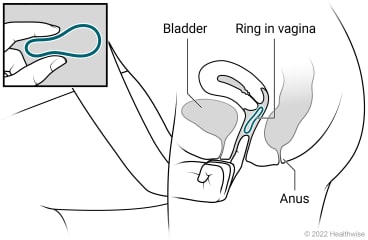
The vaginal ring is used to prevent pregnancy. It's a soft plastic ring that you put into your vagina. It gives you a regular dose of the hormones estrogen and progestin.
The ring protects against pregnancy for 1 month at a time. You wear one ring for 3 weeks in a row and then go without a ring for 1 week. During this week, you have your period. Or you may use the ring continuously. This means you don't take the ring out for a week each month. With this method, you won't have your period.
The ring is a highly effective method of birth control when it is used exactly as directed.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you use it safely?
How to use the vaginal ring
- Talk to your doctor about when to start using the ring. Ask your doctor if you need to avoid vaginal sex or use backup birth control, such as a condom, for the first 7 days.
- Insert the ring according to the package instructions. You can't put the ring in the wrong way. It works no matter what its position in the vagina is.
- Note the day you put the ring in. Leave the ring in for 3 weeks. You don't have to remove the ring when you have vaginal sex.
- When the 3 weeks are up, take the ring out on the same day of the week that you put it in. Leave the ring out for 7 days. You will have your period during these 7 days.
- After the 7-day break, put in the ring on the same day of the week that you did 4 weeks earlier. You may still be having your period.
- For continuous use, put in a new ring every 4 weeks with no ring-free break in between.
- Check with your doctor before you use any other medicines, including over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbal products, and supplements. Birth control hormones may not work as well to prevent pregnancy when combined with other medicines.
If you forget to change the ring or it comes out
Always read the label for specific instructions, or call your doctor.
- If you leave your ring in for too long or forget to replace it on schedule, follow the instructions that came with the ring. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about what to do.
- Use backup birth control or don't have vaginal sex until a new ring has been in place for 7 days. If you had unprotected vaginal sex, you can use emergency contraception to help prevent pregnancy. You can get emergency contraceptive pills without a prescription at most drugstores.
What should you think about when using the vaginal ring?
Some pros of using the ring
- The ring is more effective at preventing pregnancy than barrier methods of birth control, such as the condom or diaphragm.
- It may reduce acne, heavy bleeding and cramping, and symptoms of premenstrual syndrome.
- The ring is convenient. You insert it only 1 time each month. You don't have to interrupt sex to protect against pregnancy.
- The ring may also be used continuously, without taking it out for a week each month. This protects against pregnancy and is also a safe way to avoid having your period. This may help if you have painful periods.
Some cons of using the ring
- The ring doesn't protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as herpes or HIV/AIDS. You can use a condom to reduce your risk of getting an STI.
- The ring may cause changes in your period. You may have little bleeding, skipped periods, or spotting. If you're using the ring continuously, without taking it out for a week, you won't have periods. But you may still have breakthrough bleeding. This usually isn't harmful, and it may decrease over time.
- It may cause mood changes or less interest in sex.
- The ring contains estrogen. It may not be right for you if you have certain health problems or concerns.
- You must remember to change the ring on schedule.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if you have:
- Sudden, severe chest pain.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Sudden, severe headache.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if you have:
- Severe pain in your belly.
- Headaches that:
- Happen more often.
- Are getting worse.
- Start with auras, such as seeing spots, wavy lines, or flashing lights.
- Signs of a blood clot, such as:
- Pain in the calf, back of the knee, thigh, or groin.
- Swelling in the leg or groin.
- A color change on the leg or groin. The skin may be reddish or purplish, depending on your usual skin color.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You think you might be pregnant.
- You think you may be depressed.
- You think you may have been exposed to or have a sexually transmitted infection.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter X304 in the search box to learn more about "The Vaginal Ring for Birth Control: Care Instructions".
Current as of: May 5, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

