Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate. The prostate is part of the male reproductive system. It's a small organ below the bladder that makes fluid for semen. The prostate also releases prostate-specific antigen (PSA) into the blood. A PSA test measures the amount of PSA in your blood. A high PSA level in the blood may mean that your prostate is enlarged or infected. It could also mean that you have prostate cancer.
Screening can help find prostate cancer early. When it's found and treated early, the cancer may be cured.
In most cases, prostate cancer isn't life-threatening. This is especially true in someone who is older and when the cancer grows slowly.
Only you know which option is right for you. Work with your doctor to be sure that your decision aligns with what’s important to you. Take a few minutes to compare the options and see what you prefer.
What's involved
| Have a PSA test | Don't have a PSA test |
|---|---|
You have a blood test to check your PSA level. If it’s high, you may have more tests, such as repeat PSA tests or a prostate biopsy. |
You’ll see your doctor as needed or if you have prostate or urinary symptoms. |
Benefits
| Have a PSA test | Don't have a PSA test |
|---|---|
A PSA test can help find some prostate cancers early. When prostate cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat.
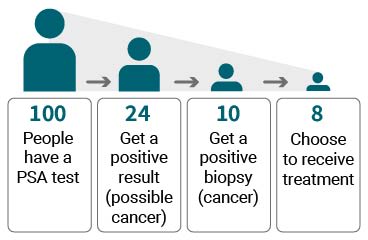
PSA testing may prevent some deaths from prostate cancer. Of those who are diagnosed with cancer and have treatment:
|
You avoid testing that could lead to a diagnosis of cancer and avoid treatments that can cause urinary, bowel, and erection problems. You may avoid invasive testing, such as a prostate biopsy. These tests could be harmful and cause worry. |
Risks
| Have a PSA test | Don't have a PSA test |
|---|---|
After a PSA test, you may have a small bruise at the test site. A PSA test may miss some cancers. Some PSA test results may be normal when there is cancer (called a false negative). A PSA test may show a high PSA level that is not caused by cancer (called a false positive).
If your PSA level is high, you may need more tests to check for cancer. These tests may include a prostate biopsy, which could be harmful and cause worry.
A PSA test may find cancers that wouldn't have caused a problem (called overdiagnosis).
Cancer treatments can cause urinary, bowel, and erection problems. Of those who have prostate cancer treatment:
|
You may miss the chance of finding prostate cancer early, when the cancer may be easier to treat. |
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter F982 in the search box to learn more about "Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Should You Have a PSA Test?".
Current as of: October 25, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

