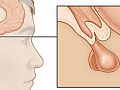
A prolactin test measures the level of the hormone prolactin, which is made by the pituitary gland, in your blood.
Pregnant women have high levels of prolactin, which helps make breast milk. During pregnancy, prolactin levels increase by 10 to 20 times. After the baby is born, prolactin stays high if you are breastfeeding. In women who do not breastfeed, prolactin levels return to normal soon after they give birth. After months of breastfeeding, prolactin levels may also return to normal levels even if you still breastfeed.
The pituitary glands of men and nonpregnant women also make prolactin, but it is not clear what it does in the body for these people.
Prolactin levels are different throughout the day. The highest levels occur during sleep and shortly after you wake up. Prolactin levels also get higher during times of physical or emotional stress.
Many medicines can cause prolactin levels to go up. Tumors of the pituitary gland can sometimes cause prolactin to be made. A damaged pituitary gland may not be able to make normal amounts of prolactin, so levels will be lower.
Why It Is Done
A test for prolactin is done:
- To find the cause of abnormal nipple discharge, or if a woman is not having periods (amenorrhea) or if a woman is having a hard time becoming pregnant (infertile).
- In a man when a pituitary gland problem is suspected. Also, a prolactin test may be done to check levels if a man lacks sexual desire or if he has trouble getting an erection (erectile dysfunction). Prolactin levels may be checked when a man's testosterone levels are really low.
- To see whether a tumor in the pituitary gland (called a prolactinoma) is making large amounts of prolactin.
How To Prepare
A blood prolactin test is usually done about 3 hours after you wake up, sometime between 8 a.m. and 10 a.m. You may be asked to fast for several hours before the test.
Emotional stress or strenuous exercise just before the test can raise prolactin levels. You may be asked to rest quietly for up to 30 minutes before having your blood drawn.
Stimulation of the nipples can raise prolactin levels. Avoid nipple stimulation for 24 hours prior to prolactin testing. A woman having abnormal nipple discharge should not do anything to cause more discharge before the test.
How It Is Done
A health professional uses a needle to take a blood sample, usually from the arm.
How It Feels
When a blood sample is taken, you may feel nothing at all from the needle. Or you might feel a quick sting or pinch.
Risks
There is very little chance of having a problem from this test. When a blood sample is taken, a small bruise may form at the site.
Results
What do the results of a prolactin blood test mean?
Normal
Each lab has a different range for what's normal. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. The normal range is just a guide. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you.
High values
- High levels of prolactin may mean a pituitary gland tumor (prolactinoma) is present. The higher the prolactin level, the more likely a tumor is present. If the level is very high, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) test may be done to confirm whether a tumor is present. A normal or low prolactin level does not always mean there is no pituitary tumor. An MRI test may be done if a tumor is suspected.
- High levels of prolactin may mean that the pituitary gland is making excess prolactin for unknown reasons (idiopathic hyperprolactinemia).
- Other conditions that can cause high prolactin levels include pregnancy, liver disease (cirrhosis), kidney disease, and hypothyroidism.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: September 25, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: September 25, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.