Overview
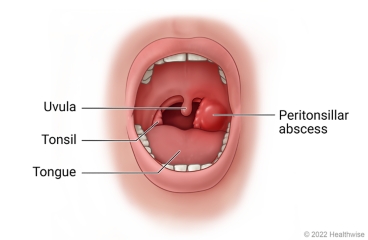
A peritonsillar abscess is a collection of pus that forms in tissues around one or both of the tonsils. It can occur as a result of strep throat or another infection. An abscess can cause severe pain and make it very hard to swallow.
You will need antibiotics. In some cases, your abscess will have been drained through a needle or small incision.
You may have had a sedative to help you relax. You may be unsteady after having sedation. It can take a few hours for the medicine's effects to wear off. Common side effects of sedation include nausea, vomiting, and feeling sleepy or tired.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and contact your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- If the doctor gave you a sedative:
- For 24 hours, don't do anything that requires attention to detail. This includes going to work, making important decisions, or signing any legal documents. It takes time for the medicine's effects to completely wear off.
- For your safety, do not drive or operate any machinery that could be dangerous. Wait until the medicine wears off and you can think clearly and react easily.
- Take your antibiotics as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
- Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- If you are not taking a prescription pain medicine, ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter medicine.
- If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed.
- Store your prescription pain medicines where no one else can get to them. When you are done using them, dispose of them quickly and safely. Your local pharmacy or hospital may have a drop-off site.
- Gargle with warm salt water once an hour to help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort. Use 1 teaspoon of salt mixed in 8 fluid ounces of warm water.
- Get lots of rest.
- Follow your doctor's instructions if your abscess was drained through a needle or small incision.
- While your throat is very sore, use liquid nourishment such as soup or high-protein drinks.
- Prevent spreading an infection. Wash your hands often, do not sneeze or cough on others, and do not share toothbrushes, eating utensils, or drinking glasses.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You have trouble breathing.
- You passed out (lost consciousness).
Contact your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or worse symptoms of infection, such as:
- Increased pain or swelling in your throat.
- A new or higher fever.
- You have new or worse nausea or vomiting.
- You have new or worse trouble swallowing.
- You have a hard time drinking fluids.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You do not get better as expected.
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

