Overview
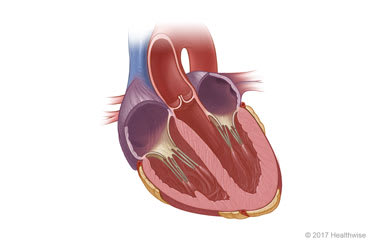
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (say "hy-per-TROH-fik kar-dee-oh-my-AWP-uh-thee") is a disease in which the heart muscle grows too thick. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is sometimes called HCM.
Many people have no symptoms and live a normal life with few problems. But some people can have problems. The thickened heart muscle can make it hard for the heart to pump blood well. This can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, fainting, and fatigue.
It also can affect the heart's electrical system. For some people, this can increase the risk for life-threatening abnormal heartbeats. Based on your risk, a device called an ICD (implantable cardioverter-defibrillator) may be an option. This device can stop these abnormal heartbeats.
Good care at home can help you cope with symptoms and manage the condition.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Take your medicines exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine. You will get more details on the specific medicines your doctor prescribes.
- If you smoke, vape, or use other tobacco or nicotine products, try to quit. If you can't quit, cut back as much as you can. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about quit programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
- Eat heart-healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and lean meats. Limit sodium, sugars, and alcohol.
- Drink plenty of fluids (unless your doctor has told you to limit fluids).
- Be active. Ask your doctor what level and types of exercise are safe for you. You may need to avoid strenuous activity.
- Stay at a weight that's healthy for you. Talk to your doctor if you need help losing weight.
- Stay up to date on vaccines against COVID-19, the flu, and pneumonia.
- Tell your family members that you have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. They may want to talk with a doctor about getting tested for this condition. Testing can identify it before it causes symptoms.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You passed out (lost consciousness).
- You have severe trouble breathing or you cough up pink, foamy mucus.
- You have symptoms of a heart attack. These may include:
- Chest pain or pressure, or a strange feeling in the chest.
- Sweating.
- Shortness of breath.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Pain, pressure, or a strange feeling in the back, neck, jaw, or upper belly or in one or both shoulders or arms.
- Lightheadedness or sudden weakness.
NOTE: If you are having heart attack symptoms, the 911 operator may tell you to chew 1 adult-strength or 2 to 4 low-dose aspirin. Wait for an ambulance. Do not try to drive yourself.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or increased shortness of breath.
- You are dizzy or lightheaded, or you feel like you may faint.
- You have sudden weight gain, such as more than 2 to 3 pounds in a day or 5 pounds in a week. (Your doctor may suggest a different range of weight gain.)
- You have increased swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet.
- You have an ICD and you have signs of infection, such as:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness.
- Red streaks leading from the cut (incision).
- Pus draining from the incision.
- A fever.
- You have a sudden episode of a skipping heartbeat or a very fast heartbeat.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if you have any problems.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter Q219 in the search box to learn more about "Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Care Instructions".
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

