Overview
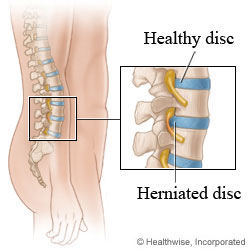
The bones that form the spine in your back are cushioned by small discs. If a disc is damaged, it may bulge or break open (herniate). A herniated disc can result from normal wear and tear as we age or from an injury or disease. If a herniated disc irritates or presses on a nerve, it can cause pain and numbness in your leg (sciatica) and/or back pain.
Your symptoms may get better on their own in a few weeks or months. Avoid movements and positions that make your pain worse. Medicine and exercise can also help. In some cases, you may need surgery.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- For most back and neck pain, you can take over-the-counter pain medicine. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and Tylenol are examples. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- If your doctor gave you prescription medicines, take them exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine.
- Avoid movements and positions that increase your pain or numbness.
- Improve your posture. Slumping or slouching alone may not cause low back pain. But after the back has been strained or injured, bad posture can make pain worse.
- Try taking short walks and doing light activities that do not cause pain. Even if you are feeling some pain, it is important to keep your muscles active and strong.
- Use heat or ice to relieve pain.
- To apply heat, put a warm water bottle, heating pad set on low, or warm cloth on your back. Do not go to sleep with a heating pad on your skin.
- To use ice, put ice or a cold pack on the area for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your skin.
- Do exercises that your doctor or physical therapist suggests. These may include core stabilization exercises. These will help keep your back muscles strong and prevent another injury.
- Stay at a healthy weight. This may reduce the load on your back.
- Quit smoking if you smoke. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
- To avoid hurting your back when lifting:
- Lift with your legs, not your back, by squatting and bending your knees. Avoid bending forward at the waist when lifting.
- Rise slowly.
- Keep the load as close to your body as possible, at the level of your belly button.
- Avoid turning or twisting your body while holding a heavy object.
- Get help if you need to lift a heavy object. Never lift a heavy object above shoulder level.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You are unable to move a leg at all.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or worse symptoms in your arms, legs, chest, belly, or buttocks. Symptoms may include:
- Numbness or tingling.
- Weakness.
- Pain.
- You lose bladder or bowel control.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You are not getting better as expected.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter F534 in the search box to learn more about "Herniated Disc: Care Instructions".
Current as of: July 24, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

