Overview
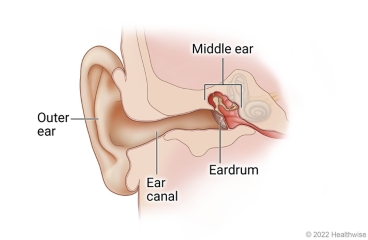
The most frequent kind of ear infection in babies is called otitis media. This is an infection behind the eardrum, in the middle ear.
It may start with a cold. It can hurt a lot. Children with ear infections often fuss and cry, pull at their ears, and sleep poorly.
Ear infections are common in babies and young children.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the ear infection. Children under 6 months are usually given an antibiotic. If your child is over 6 months old and the symptoms are mild, antibiotics may not be needed. Your doctor may also recommend medicines to help with fever or pain.
Follow-up care is a key part of your child's treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if your child is having problems. It's also a good idea to know your child's test results and keep a list of the medicines your child takes.
How can you care for your child at home?
- Give your child acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) for fever, pain, or fussiness. Do not use ibuprofen if your child is less than 6 months old unless the doctor gave you instructions to use it. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- If the doctor prescribed antibiotics for your child, give them as directed. Do not stop using them just because your child feels better. Your child needs to take the full course of antibiotics.
- Place a warm washcloth on your child's ear for pain.
- Try to keep your child resting quietly. Resting will help the body fight the infection.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think your child may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- Your child is extremely sleepy or hard to wake up.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- Your child seems to be getting much sicker.
- Your child has a new or higher fever.
- Your child's ear pain is getting worse.
- Your child has redness or swelling around or behind the ear.
Watch closely for changes in your child's health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- Your child has new or worse discharge from the ear.
- Your child is not getting better after 2 days (48 hours).
- Your child has any new symptoms, such as hearing problems, after the ear infection has cleared.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter V807 in the search box to learn more about "Ear Infection (Otitis Media) in Babies 0 to 2 Years: Care Instructions".
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

