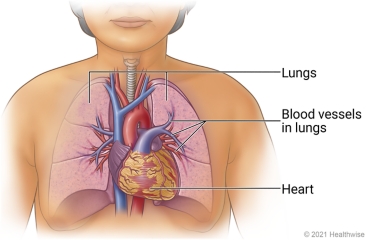
What is pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary edema is the buildup of fluid in the lungs. It usually happens when the heart does not pump blood through the body as well as it should. Blood can back up into the blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the heart. Blood pressure rises in those blood vessels, and fluid is pushed into the lungs. This makes it hard to breathe. Other symptoms include a new irregular or rapid heartbeat and coughing up foamy, pink mucus.
Pulmonary edema can also be caused by another disease, such as liver or kidney failure. It can also happen at high altitudes, from a poisoning, or by a nonfatal drowning.
A chest X-ray and a blood test are often used to identify this condition.
Pulmonary edema is serious. You may need special care, such as being in the intensive care unit (ICU). This may worry you. But the hospital staff understands this. They will explain what happens and will answer your questions.
How is it treated?
The goal of treatment is to relieve the fluid buildup in your lungs and help you breathe more easily. The doctor may:
- Give you medicines to help relieve the fluid buildup.
- Give you oxygen through the nose or a face mask. You may need a breathing machine (ventilator) and have a breathing tube placed into your windpipe (intubation).
Your treatment also depends on what caused the edema. For example, you may also get medicines to help your heart pump blood more easily. You may get medicine through a vein (I.V., or intravenously).
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.