What is histoplasmosis?
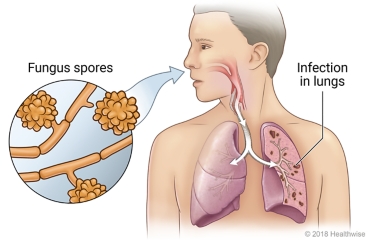
Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by a type of fungus (or mold). It most often affects the lungs. In the United States, the fungus is most common in central and eastern parts of the country. It's often found in the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys, but it can be found in other places.
What causes it?
A person can get infected by breathing in the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. This fungus often grows in soil that contains bat or bird droppings. You can get infected if you're in an area where the fungus lives. This is more likely if you're doing an activity that stirs up soil that has the fungus in it.
The infection doesn't spread from one person to another.
Some people have a higher risk of getting sick if exposed to this fungus. They include:
- Infants.
- Older adults.
- People who have a weakened immune system. (Having an organ or tissue transplant or a condition such as HIV or AIDS may cause this.)
- People who take certain medicines that weaken the immune system, such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy.
What are the symptoms?
Most people don't have symptoms. But the infection can make you feel like you have the flu. You may have a fever, a cough, chills, chest pain, a headache, and fatigue.
Symptoms usually get better on their own within several weeks. Severe infections may last longer. In some cases, the infection may go away but come back years later.
In people who have a weakened immune system, the infection may spread from the lungs to other organs, such as the brain.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will do a physical exam. The doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and past health. The doctor may ask about your activities or places you've traveled that could have raised your risk of getting the infection.
You may have tests to check for infection. These include:
- Blood or urine tests.
- Imaging tests, such as a chest X-ray or a CT scan of the lungs.
- A fluid or tissue sample (biopsy). In more severe cases, a sample may be taken from the lungs or respiratory tract or from the fluid that normally surrounds the spinal cord.
Current as of: September 30, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

