Overview
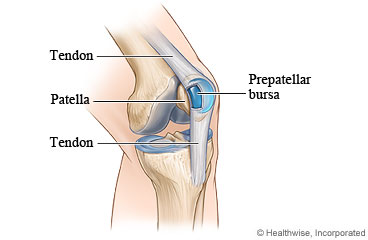
Bursitis is inflammation of the bursa. A bursa is a small sac of fluid that cushions a joint and helps it move easily. Bursitis of the kneecap is inflammation of the bursa found between the front of the kneecap and the skin. Kneeling for a long time can cause kneecap bursitis, which can develop into an egg-shaped bump on the front of the kneecap.
Bursitis usually gets better if you avoid the activity that caused it. If it lasts or gets worse despite home treatment, your doctor may draw fluid from the bursa through a needle. This may relieve your pain and help your doctor know if you have an infection. If so, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. If you have inflammation only, you may get a corticosteroid shot to reduce swelling and pain. Your doctor may recommend physical therapy and stretching activities. Rarely, surgery is needed to drain or remove the bursa.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Put ice or a cold pack on your kneecap for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your skin.
- After 3 days of using ice, you may use heat on your kneecap. You can use a hot water bottle, a heating pad set on low, or a warm, moist towel.
- Prop up the sore leg on a pillow when you ice it or anytime you sit or lie down during the next 3 days. Try to keep it above the level of your heart. This will help reduce swelling.
- Rest your knee. Stop any activities that cause pain. Switch to activities that do not stress your knee.
- Take your medicines exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine.
- Ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve). Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- To prevent and ease kneecap bursitis during work, play, and daily activities:
- Wear kneepads when kneeling on hard surfaces. Avoid kneeling for too long at a time.
- Strengthen and stretch your leg muscles.
- Avoid deep knee bends.
- You can slowly return to the activity that caused the pain, but do it with less effort until you can do it without pain or swelling. Be sure to warm up before and stretch after you do the activity.
When should you call for help?
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have a fever.
- You have increased swelling or redness in your knee area.
- You cannot use your knee, or the pain in your knee gets worse.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You have pain for 2 weeks or longer despite home treatment.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter H649 in the search box to learn more about "Kneecap Bursitis: Care Instructions".
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

