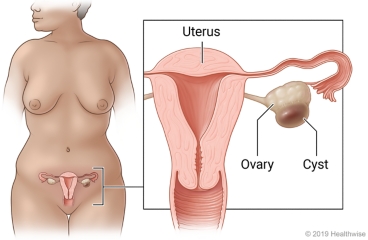
Overview
An ovarian cyst is a sac that forms on the ovary and swells up with fluid. If the cyst bleeds, it is called a hemorrhagic (say "heh-muh-RA-jick") ovarian cyst. If a hemorrhagic cyst breaks open, it can release blood and fluid into the lower belly and pelvis.
You may not have symptoms from the cyst. But if it is large, or if it twists or breaks open, you may have pain or other problems. You may feel pain from the cyst or have symptoms from losing blood.
Your doctor may use a pelvic ultrasound to see if you have a cyst. Blood tests can help your doctor tell if the cyst is bleeding or you have lost a lot of blood.
Treatment depends on your symptoms. If they are mild, your doctor may suggest carefully watching your symptoms and doing blood tests again. But if you have a cyst that is very large, bleeds a lot, or causes other problems, your doctor may suggest surgery to remove it. If the bleeding is heavy, you may also need treatment to replace the blood.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.