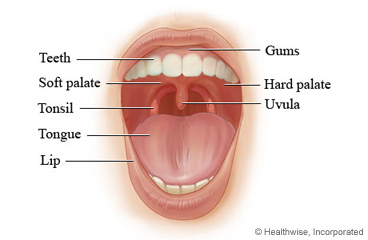
Overview
Glossitis is swelling of the tongue. The tongue looks smooth and may be an unusual color from pinkish to dark red. Glossitis is often caused by an infection. Other causes include injury, irritation from tobacco or spicy foods, or a poor diet.
Glossitis can make it hard for you to talk, chew, or swallow, especially if you get sores on your tongue.
Treatment for glossitis depends on the cause. An infection is treated with antibiotics. Other medicines can relieve swelling and pain. If the swelling is severe, your doctor may prescribe steroids.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.