Good nutrition in a baby's first year is important for healthy growth and development. This is a time of many changes for your baby. For example, your baby will move from drinking breast milk or formula to eating solid foods. And feeding is a time for bonding with your baby.

Ages 0 to 5 months: For about the first 6 months, breast milk or iron-fortified infant formula can give all the nutrition and fluids your baby needs.

Ages 6 to 12 months: At about 6 months, babies are often ready to try cooked, soft food. They will show signs that they are ready. They may open their mouth when food is offered, hold their head up, and try to sit without support.
How can you feed your baby in the first year?
Feeding your baby for months 0 to 5
- Feed your baby whenever they are hungry.
- Look for signs of hunger such as hand-sucking or lip-smacking.
- Your baby may be full if they slow down or turn away while feeding.
- If you're breastfeeding, ask your doctor if your baby needs vitamin D or another supplement.
Introducing solid foods
- Offer small portions. A serving might be 1 to 2 tablespoons at first.
- You can give your baby food that is blended, mashed, or soft and cut small. Try soft vegetables, iron-fortified infant cereals, proteins, and fruits.
- Maybe you'll feed your baby with a small spoon. Or your baby may be able to do it on their own. This may vary by the meal.
- When your baby can easily eat soft foods, try chopped or ground food.
Serving snacks and new foods
- Try offering food 2 or 3 times a day. Breast- or bottle-feed in between those times.
- Offer a variety of foods. Try new colors, textures, and flavors of food. You may have to offer a new food many times before your baby accepts it.
Practicing safe and healthy feeding

- For foods that may cause an allergic reaction, introduce them a few days apart. These foods include nut butters, milk, eggs, and wheat. Watch for signs of allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling, and vomiting.
- To introduce a food that may cause an allergic reaction, try giving a small amount with a food your baby has had before. For example, try mixing some peanut butter into oatmeal.
- Avoid foods that may cause your baby to choke. Cut or smash hot dogs and grapes into small sizes, and cook hard vegetables like carrots.
- Feed your child solid food while they are sitting up in a high chair. Have an adult with your child to help prevent choking.
- Look for signs that your baby is full. Stop if your baby is full or doesn't like the food.
- At about 6 months, once they're eating solid foods, let your baby drink from a cup. Breast milk, formula, and water are the best options. Start with 4 to 8 ounces a day.
How can you introduce a bottle to a breastfed baby?
Experts recommend feeding your baby only breast milk for the first year. Using a bottle may help all caregivers feed your baby. Talk to your doctor if you plan to switch from breastfeeding to bottle-feeding. Here are some tips.
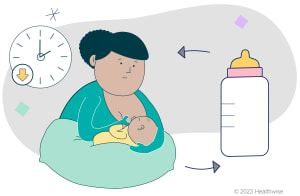
Slowly reduce the number of times you breastfeed each day. Offer the bottle before each breastfeeding. Each week, choose one more breastfeeding time to replace or shorten with bottle-feeding.

Wean your baby slowly. Pumping breast milk will allow you to save milk to use later in a bottle. Using both breast- and bottle-feeding as needed may help you return to work or do other things.
Current as of: October 24, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

