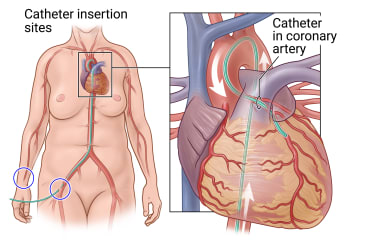
What is a coronary angiogram?
A coronary angiogram is a test to look at the large blood vessels of your heart (coronary arteries). These blood vessels feed blood, oxygen, and nutrients to your heart muscle.
Why is this test done?
This test is done to check blood flow in your coronary arteries. It can show the size and location of narrowed or blocked sections of an artery.
How is the test done?
- You may get medicine to help you relax.
- A thin tube called a catheter is put into a blood vessel in your groin or wrist.
- You will get a shot to numb the skin where the catheter goes in. You may feel pressure when the doctor moves the catheter through your blood vessel into your heart.
- Dye is put into your coronary arteries through the catheter. Your doctor can see the dye as it moves through the arteries. This lets your doctor look for areas that are narrowed or blocked.
- You may feel hot or flushed for several seconds when the dye is put in.
- If you have a narrowed or blocked artery, the doctor may do an angioplasty or a coronary stent procedure. These procedures make more room for blood to flow.
How long does it take?
The test may take about 1 hour. But you need time to get ready for the test and time to recover. If you also have angioplasty and possibly a stent placed after the test, the whole procedure may take a few hours.
What happens after the test?
- You will stay in a room for at least a few hours to make sure the catheter site starts to heal. You may have a bandage or a compression device on your groin or wrist to prevent bleeding.
- If the catheter was placed in your groin, you will lie in bed with your leg straight for up to a few hours. If the catheter was put in your wrist, you will need to keep your arm still for at least 1 hour.
- You may be able to go home later the same day, or you may need to stay in the hospital overnight. You will get more instructions for what to do at home.
- Drink plenty of fluids for several hours after the test. If you have kidney, heart, or liver disease and have to limit fluids, talk with your doctor before you increase the amount of fluids you drink.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter X053 in the search box to learn more about "Coronary Angiogram: About This Test".
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

