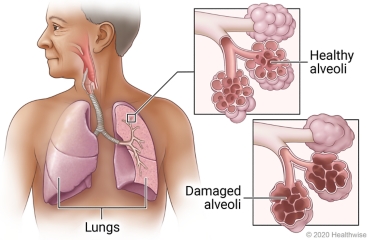
Overview
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) is a protein normally found in your lungs, liver, and blood. It helps protect tissues in your body from damage.
Some people do not make enough AAT in their bodies. Some people make abnormal AAT. Both of these problems are called AAT deficiency. It is passed down by genes that you inherit from your parents.
People who have AAT deficiency may get emphysema at a young age, such as 30 or 40 years old, especially if they smoke. Some people get liver or skin problems. If you have AAT deficiency but do not smoke, you may not get emphysema.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
To stay healthy
- If you smoke, try to quit or cut back as much as you can. Not smoking is the most important step you can take to prevent lung problems. It is never too late to stop. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
- Try to avoid infections such as COVID-19, colds, and the flu. Wash your hands often. You may want to wear a mask when you go to public indoor spaces. Try to avoid sick people.
- Stay up to date on your vaccines. Talk to your doctor about which vaccines are right for you. Ask your doctor if you should get hepatitis vaccines.
- Try to avoid things that could hurt your lungs. These include chemical fumes, factory dust, soot, and air pollution. Talk to your doctor about ways to protect yourself if you are exposed to substances that irritate your lungs at home or at work.
- Try to avoid getting infections that could hurt your liver. Practice safer sex. Ask your doctor about PrEP. If you inject drugs, don't share needles or injection supplies.
- If you drink alcohol, try to quit. It can hurt your liver. Talk to your doctor if you need help.
Medicines
- Take your medicines exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine.
Activity
- Be active. For many people, walking is a good choice. Or you may want to swim, bike, or do other activities. Try to be active every day.
- Be active. Talk to your doctor about what type, amount, and level of exercise is safe for you.
Eating healthy
- Eat healthy foods. These foods include vegetables, fruits, nuts, beans, lean meat, fish, and whole grains.
- Limit sodium and sugar.
Mental health
- Talk to your family or friends or a therapist about your feelings. Some people feel frightened, angry, hopeless, helpless, and even guilty. Talking openly about feelings may help you cope. If these feelings last, talk to your doctor.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You have severe trouble breathing.
- You have severe chest pain.
- You vomit blood or what looks like coffee grounds.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or worse trouble breathing.
- You have new or worse chest or belly pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have a fever.
- You feel very sleepy or confused.
- There is a new or worse yellow tint to your skin or the whites of your eyes.
- You have any abnormal bleeding, such as:
- Nosebleeds.
- Vaginal bleeding that is different (heavier, more frequent, at a different time of the month) than what you are used to.
- Bloody or black stools or rectal bleeding.
- Bloody or pink urine.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- Your belly is getting bigger.
- You are gaining weight.
- Your symptoms get worse.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter X830 in the search box to learn more about "Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) Deficiency: Care Instructions".
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

