What is it?
An albumin-creatinine ratio test compares the amounts of albumin and creatinine in your urine.
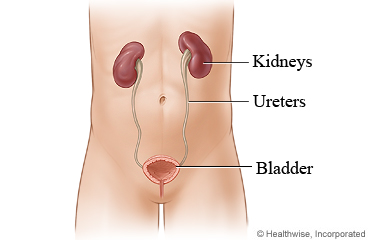
Albumin (say "al-BYOO-mun") is normally found in the blood. When the kidneys are damaged, small amounts of albumin leak into the urine.
Creatinine (say "kree-AT-uh-neen") is a waste product found in urine.
Why is this test done?
This test helps your doctor see how well your kidneys are working. It is done most often to check the kidneys in people with diabetes. It may also be done to check people with high blood pressure, heart failure, and cirrhosis.
How do you prepare for the test?
In general, you don't need to prepare before having this test. Your doctor may give you some specific instructions.
How to do the test
- Open the wipes. Remove the lid from the container, and set it down with the inner surface up.
- Wash your hands before you collect the urine.
- Clean your genitals with the provided wipes.
If you have a vulva, hold the folds of skin or lips (labia) apart. Wipe the area from front to back. If you have a penis, use the wipes to clean the tip. If you have a foreskin, pull it back.
- Start to urinate into the toilet or urinal for a few seconds. Keep holding your skin away from the urine stream.
- After the urine has flowed for several seconds, place the collection container in the stream. Collect about 2 ounces (a quarter cup).
- Don't touch the container to your genitals.
- Finish urinating into the toilet or urinal.
- Carefully replace the lid on the container.
- Wash your hands.
How to do the test
You collect your urine for a period of time, such as over 4 or 24 hours. Your doctor will give you a large container that holds about 1 gallon. A small amount of preservative may be in the container. You will use the container to collect your urine.
- When you first get up, you empty your bladder.
But don't save this urine. Write down the time you began.
- For the set period of time, collect all your urine.
Each time you urinate during this time period, collect your urine in a small, clean container. Then pour the urine into the large container. Don't touch the inside of either container with your fingers.
- Don't get toilet paper, pubic hair, stool (feces), menstrual blood, or anything else in the urine sample.
- Keep the collected urine in the refrigerator for the collection time.
- Empty your bladder for the last time at or just before the end of the collection period.
Add this urine to the large container. Then write down the time.
What happens after the test?
- Follow your doctor's instructions for taking the urine to the doctor's office or lab.
- You can go back to your usual activities right away.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to keep a list of the medicines you take. Ask your doctor when you can expect to have your test results.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter A552 in the search box to learn more about "Albumin-Creatinine Ratio: About This Test".
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

