Your Care Instructions
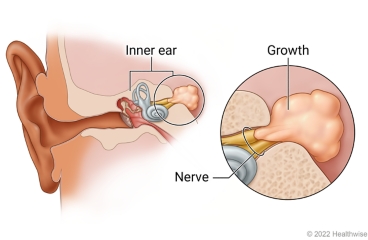
An acoustic neuroma is a growth (tumor) on the nerve to the inner ear. It does not turn into cancer. But it can cause hearing loss, ringing in the ear, and dizziness. A large acoustic neuroma can press on the brain and become life-threatening.
Acoustic neuromas usually grow very slowly. They are most common in people between the ages of 30 and 60.
Your doctor may want to watch a small neuroma to see how fast it grows. You may get regular tests to watch its growth. Neuromas that cause problems may be treated with radiation or surgery. An acoustic neuroma that is removed does not usually grow back.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Protect your ears from loud sounds. This can prevent hearing loss from getting worse.
- Try hearing aids if you have trouble hearing.
- Think about joining a support group. Sharing your experiences with other people who have the same problem may help you learn more and cope better.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You have symptoms of a stroke. These may include:
- Sudden numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of movement in your face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of your body.
- Sudden vision changes.
- Sudden trouble speaking.
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding simple statements.
- Sudden problems with walking or balance.
- A sudden, severe headache that is different from past headaches.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You are dizzy or lose your balance.
- You lose hearing in one ear.
- Part of your face droops or sags.
- You have vision problems, such as blurred or double vision, or you can see only out of one eye.
- You slur your words or cannot talk normally.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You do not get better as expected.
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

