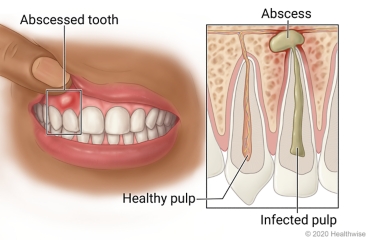
Overview
An abscessed tooth is a tooth that has a pocket of pus in the tissues around it. Pus forms when the body tries to fight an infection caused by bacteria. If the pus cannot drain, it forms an abscess. An abscessed tooth can cause red, swollen gums and throbbing pain, especially when you chew. You may have a bad taste in your mouth and a fever, and your jaw may swell.
Damage to the tooth, untreated tooth decay, or gum disease can cause an abscessed tooth.
An abscessed tooth needs to be treated by a dental professional right away. If it is not treated, the infection could spread to other parts of your body. Your dentist will give you antibiotics to stop the infection. If antibiotics don't stop the infection, you may need other treatments.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Brush and floss gently.
- Reduce pain and swelling in your face and jaw by putting ice or a cold pack on the outside of your cheek. Do this for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your skin.
- Avoid using tobacco products. Tobacco and nicotine slow your ability to heal.
- Take pain medicines exactly as directed.
- If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed.
- If you are not taking a prescription pain medicine, ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter medicine such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin). Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- Take antibiotics as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You have trouble breathing.
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or worse symptoms of infection, such as:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You do not get better as expected.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter L466 in the search box to learn more about "Abscessed Tooth: Care Instructions".
Current as of: September 30, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

