Your Care Instructions
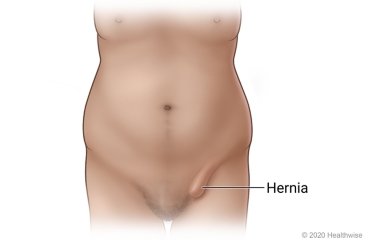
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue bulges through a weak spot in your groin area. You may see or feel a tender bulge in the groin or scrotum. You may also have pain, pressure or burning, or a feeling that something has "given way."
Hernias are caused by a weakness in the belly wall. The bulge or discomfort may occur after heavy lifting, straining, or coughing. Hernias do not heal on their own, and they tend to get worse over time.
If your hernia does not bother you, you most likely can wait to have surgery. Your hernia may get worse, but it may not. In some cases, hernias that are small and painless may never need to be repaired.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Take pain medicines exactly as directed.
- If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed.
- If you are not taking a prescription pain medicine, ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter medicine.
- Use proper lifting techniques, and avoid heavy lifting if you can. To lift things more safely, bend your knees and let your arms and legs do the work. Keep your back straight, and do not bend over at the waist. Keep the load as close to your body as you can. Move your feet instead of turning or twisting your body.
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
- Include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains in your diet each day. These foods are high in fiber and will make it easier to avoid straining during bowel movements.
- Do not smoke. Smoking can cause coughing, which can cause your hernia to bulge. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good.
When should you call for help?
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have new or worse belly pain.
- You are vomiting.
- You cannot pass stools or gas.
- You cannot push the hernia back into place with gentle pressure when you are lying down.
- The area over the hernia turns red or becomes tender.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if you have any problems.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter J063 in the search box to learn more about "Inguinal Hernia: Care Instructions".
Current as of: October 19, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

