Overview
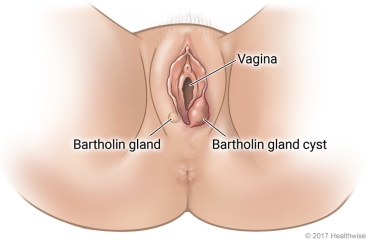
The Bartholin glands are two small organs that are located on each side of the vaginal opening. The glands are normally about the size of a pea. They produce fluid to lubricate the vagina and vulva through a small opening. If the opening is blocked, the gland swells with fluid and forms a cyst. Bartholin gland cysts are often small and painless. But if a cyst gets infected by bacteria, it can grow and become red and painful. This is called an abscess. If a cyst is infected, large, or painful, it may need to be drained.
You may have had a small tube (catheter) placed into the cyst or minor surgery to let the cyst drain. The tube will usually be left in for about 4 weeks. If you have an infection, your doctor may do a lab test to find out what kind of bacteria caused the infection. And you may get antibiotics to treat the infection.
You may have some drainage from the cyst for a few weeks.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
- Sit in a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) for 15 to 20 minutes 3 times a day. Then pat the area dry. The warm water helps the area heal and eases discomfort.
- Ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter pain medicine such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve). Read and follow all instructions on the label.
- Do not take two or more pain medicines at the same time unless the doctor told you to. Many pain medicines have acetaminophen, which is Tylenol. Too much acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be harmful.
- Wear panty liners or pads if you have discharge from the draining cyst.
- If you are sexually active, ask your doctor when it is okay for you to have sex.
- If you had a catheter placed in the cyst to help it drain, follow your doctor's instructions for activities until the tube comes out.
When should you call for help?
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
- You have symptoms of a new or worse infection, such as:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Increased drainage from the area.
- A fever.
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- The catheter falls out.
- You are not getting better as expected.
Where can you learn more?
Go to http://www.healthwise.net/patientEd
Enter P544 in the search box to learn more about "Bartholin Gland Cyst in Teens: Care Instructions".
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

